GCSE Business Studies 0450
Business Studies – External Influences
- Understand the Business Cycle and stages economies go through
- Government control over the economy by using fiscal and monetary policies
- Impact of changes in Interest Rates (monetary policy)
- Environmental and ethical issues in business and the importance of globalisation
- The Impact of Exchange Rates
The Business Cycle
Economies go through a cycle of ups and downs in the value of economic activity. These ups and downs can be measured by the gross domestic product (GDP) within a country’s economy. The business cycle consists of four main stages which are growth, boom, recession, and slump.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP is the total value of products and services produced within a country, usually over a year. GDP can also be measured quarterly (every four months) for individual countries or even the world. When GDP increases a country’s economy grows due to more activity. Global GDP can be used to understand if the world’s economic activity is growing or declining.
Fiscal Policy (Taxation and Spending)
Fiscal policy is when the government changes tax rates or spending within a country. Governments around the world will use fiscal policy (tax or spending) to influence the economic activity within their country to achieve economic objectives.
Monetary Policy (Interest Rates)
Governments can change interest rates to achieve economic objectives. Governments around the world have been increasing interest rates to combat rising inflation following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Government control over the economy
Macroeconomic policy
Governments will use macroeconomic policies to achieve the economic objectives of their country. Macroeconomic policies used by governments can be divided into fiscal or monetary actions to control or stimulate the economy. These policies are designed to work on the whole economy.
Main taxes affecting businesses
- Corporation tax – Tax on profits earned by a business
- Income Tax – Charged based on the employee’s income
- National Insurance – NHS contributions paid by employees
- Value-added tax (“VAT”) tax charged on sales
- Council tax: local tax charged by local authorities
- Customs and excise duties – Taxes paid on importing and exporting
Impact of Interest Rates
An interest rate is the amount charged for borrowing money. The Bank of England sets interest rates for the U.K. based on the government’s economic objectives (monetary policy). Interest can also be gained on savings held within a bank account. As interest rates go up or down banks will change more or less interest on money borrowed in the form of a bank loan.
When interest rates are low, consumers tend to borrow more money as the cost of borrowing is reduced. This increases demand as money is being put back into the economy by spending more on products and services.
The Unemployment Rate
Unemployment refers to a situation where people who are able and willing to work cannot find a job. The unemployment rate is based on the population of working-age (15 to 65 years) people within the country.
Unemployment rate = unemployed / labour force x 100
Environmental and Ethical impacts
Just because doing something is legal does not make it ethical. Business ethics refers to moral guidelines that govern business decisions and behaviour. Businesses can operate in a (good) ethical manner or (bad) unethical manner. These are rules and guidelines on business behaviour that all employees must follow. Employees must behave in a morally acceptable manner. Business ethics apply to all aspects of business conduct.
External Costs are costs paid for by society other than the business, as a result of business activity. External Benefits are gains to society, other than the business, resulting from business activity
Unethical business activities
- Buying from supplies that use child labour
- Exploiting suppliers by demanding and paying low prices
- Wilful selling of harmful products
- Not paying a fair wages or salaries
- Avoiding paying tax
- Paying bribes to receive contracts
- Polluting the environment
- Target advertisements at children
- Overcharging customers or being dishonest
- Failure to give correct or accurate information
- Testing cosmetics products on animals
Ethical business behaviour
- Making business profits in an honest manner
- Being fair to all stakeholder groups
- Avoiding discrimination against employees and stakeholder groups
- Protecting the environment
Advantages of good business ethics
- Gain more customers and increase customer royalty
- The business could be offered government contracts
- Attract qualified and experienced employees
- Avoid expensive court cases
Globalisation
Globalisation is a process in which economies have become increasingly integrated and interdependent this is due to increased global transportation and information leading to a more accessible global market for businesses. One advantage to businesses of globalisation is access to new markets (customers). A disadvantage is the increased amount of competition. Globalisation can reverse when the growth of world trade in goods and services (GDP) declines this occurred during the 2008 global financial crisis. There is also a growing trend in glocalisation when businesses choose to operate locally rather than globally.
Further understanding
Globalisation has led to more choices and lower prices for consumers. However, it has forced businesses to seek ways of increasing efficiency. Inefficient small businesses have gone out of business. Many companies have merged with foreign businesses to make it easier to sell in new foreign markets. This is one of the reasons behind the growth of multinational organisations.
There are several reasons for the increase in global trade, movement of products, people and capital (globalisation).
- Increased free trade agreements between countries.
- Improved communication and cheaper travel links
Multinationals
Remember a multinational business must produce goods or services in more than one country. Not just export or sell to more than one country.
Exchange Rates
Effects of Exchange Rate Depreciation
Exchange rate depreciation occurs when the value of a currency falls in comparison to another. For example, if the British Pound falls from £1=$1.80 to £1=$1. This would make imports from America more expensive for British businesses who rely on importing supplies from the USA
- Imports become expensive and exports cheaper
- This can lead to a BOP surplus. A situation where exports exceed imports
- The external debt of the country will increase
- Local goods become more competitive in the global economy
Currency depreciation can reduce living standards, weaken economic growth, and increase inflation within countries that rely on importing goods. However, depreciation can also increase GDP. This means that governments will often aim to keep the value of a currency lower to help facilitate economic recovery.
Exchange rates
The exchange rate is the value of a nation’s currency in terms of another currency such as £1=$1.40. Exchange rates are impacted by the demand and supply of a currency in a free market economy.
The exchange rate can move up (appreciate) or down (depreciate) due to changes in the demand or supply conditions.
Effects of Exchange Rate Appreciation
The exchange currency of a country appreciates when it rises in value in comparison to another country’s currency. The following image shows the exchange rate of £1 = $1.26 on December 5th 2023.
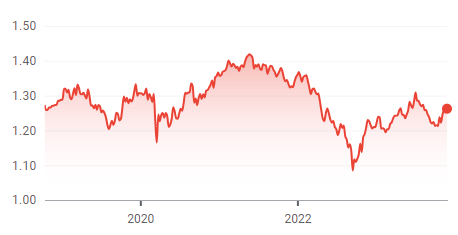
- Imported raw materials become cheaper
- Demand may shift from local to foreign-produced goods
- This can lead to a Balance of Payments (BOP) deficit as exports become expensive and imports cheaper.
Exam Tips for Exchange Rates
Remember to check if the business is importing or exporting. You can get application marks and ensure to understand the impact of the exchange rates correctly. Using SPICED will help you to remember – Strong Pound, Imports will be Cheaper and Exports Dearer (more expensive).
GCSE Business Studies Operations Management Exam Practice.
GCSE Business Studies Revision Videos

Business Activity
Coming soon…

Types of business
Coming soon…

Exam Practice for Paper One
Coming soon…
Access additional Business Studies resources
Complete our contact form and let us know what topics you would like to improve.
