GCSE Business Studies 0450
Business Studies – Marketing
- The nature and purpose of marketing
- Revision notes to provide an overview of marketing
- The marketing mix – Product, Price, Place and Promotion
- Market research and segmentation
- The product life cycle
The role of marketing
For an entrepreneur or business to succeed, it is important to identify and satisfy customers’ needs. Often entrepreneurs spot a need for a product or service (gap in the market). The four main customer needs that an entrepreneur or business must consider are price, quality, choice and convenience.
The importance of market research
Generating sales is easier when a business has a good understanding of its customers’ wants and needs. Market research enables a business to provide products or services that directly meet customer requirements.
Market research is when a business gathers, analyses and interprets information about a market. Primary Market research is information that is gathered by the business. The business gains unique information as they have collected the information first-hand. (Field Research). Secondary Market research is information that has already been collected and available. (Desk Research)
Definition of marketing
Marketing identifies customer wants and needs for the business to satisfy them profitably. This is done by ensuring that all four elements of the marketing mix are correct. Product, place, price and promotion. (Remember marketing is much more than promotion)
Market or product-orientated
Product-orientated businesses focus efforts on the product or service and believe that if the product is good customers will buy. Market-orientated is when the business researches to find out what customers want and provides the product or service based on customer wants.
3. Market Segmentation
Markets can be segmented, according to age, socioeconomic grouping, location, gender and more.
Definition
.
.
- Segmentation divides a market into different identifiable types (segments) enabling a business to target its products and services.
- Segmentation is usually based on socioeconomic grouping (income), age, location, gender, lifestyle or even the use of the product.
- Each market segment will require different methods of promotion and distribution.
- Products aimed towards teachers would be distributed through popular educational stores and products for Doctors would be advertised in exclusive medical journals.
- Better matching of customer needs – Customer needs differ. Creating separate products for each segment makes sense.
- Retain more customers – By marketing products that appeal to customers’ identifiable characteristics, a business can retain customers who might otherwise switch to competitors
- Production costs might be high as a result of marketing several different product variations.
- Extensive market research is needed.
3. The Product Life Cycle
Definition of the Product Life Cycle
The Product Life cycle describes the stages a product will go through, starting with the introduction, growth, maturity, saturation and finally decline. Each stage is based on the sales of the product. Different products will have different lengths of time for each stage of their life cycle. PlayStation has on average a five-year life cycle.
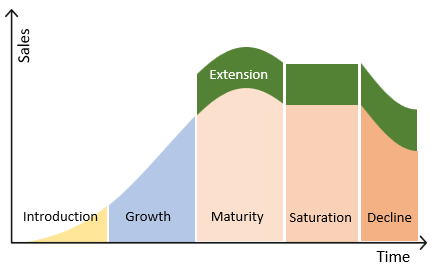
Product Life Cycle Extensions
Extension strategies are designed to extend the length of time a product’s life cycle will last. This can be done by lowering prices, advertising, enhancing the product, re-packaging and repositioning the product into a different market segment. It’s best to implement extensions during the maturity stage.
Introduction stage
The product is launched and introduced into the market. Sales figures are small and only grow slightly as the product needs to become known.
Growth stage
During the growth stage, the sales outweigh the costs. Some additional marketing may be required due to copycats. Customers are starting to become aware of the product, and sales are growing. Businesses will attempt to prolong the ‘Growth’ stage to gain market share.
Maturity
Sales are increasing more gradually during the maturity stage of the life cycle. This slowdown in sales is usually due to the increased amount of competition as other businesses will attempt to sell and complete within the same market. It is recommended to increase advertising during this stage to maintain profits or market share.
Saturation
The saturation point is where sales have reached the highest point of the life cycle. Competition is usually fierce during this stage but it’s unlikely for new competitors to come into the market. Profits can decline during this stage as more spending on marketing is required to maintain sales. It is often during the saturation stage that businesses will cut prices to try and maintain sales.
Decline
Sales decline as newer products are available. Customers will buy a newer product instead, this is usually where a business will consider replacing the product with a new one or removing the product from the market. During this stage spending on marketing is not likely to help as prices have already been lowered. The business must already launch a new product or else the business will have no sales until a new product can be introduced to the market.
.
Cost-plus Pricing is simply when a business adds the profit they would like to make based on the cost of making the product.
Competitive Pricing is when a business sets prices to match competitors or slightly below if they want to gain additional market share. This strategy can help a business avoid a price war.
Penetration Pricing is when a business sets prices lower than competitors to enter a new market.
Price Skimming is done by setting a high price, usually for a new product with demand. Mobile phone manufacturers are well known for this method of pricing when they launch the latest mobile phone.
Promotional Pricing is used to sell a product or service at a low price for a limited time.
Dynamic Pricing is used to charge different prices based on the level of demand. Airlines use dynamic pricing to charge different prices for booking a flight based on the number of seats booked. Customers taking the same flight can pay different prices based on when they booked the ticket.
The Marketing Mix
The marketing mix consists of four elements which are, product, place, price and promotion. A business will use the marketing mix to coordinate all the activities to sell (goods) products or services. (At GCSE business you only need to remember the four P’s of the marketing mix).

Pricing methods
Businesses will need to make decisions for the Price element of the marketing mix. A good starting point is for the business to consider the most appropriate pricing method. This could be based on market research, competition, business objectives or even the product or service being sold. The following provides a brief overview of the pricing methods we cover in GCSE business.
GCSE Marketing Exam Practice: Try to answer these questions before checking your answer.
GCSE Business Studies Revision Videos

Business Activity
Coming soon…

Types of business
Coming soon…

Exam Practice for Paper One
Coming soon…
Access additional Business Studies resources
Complete our contact form and let us know what topics you would like to improve.
